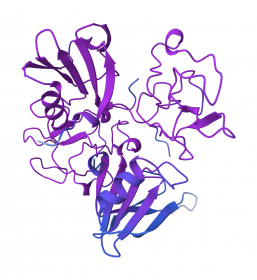
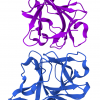
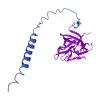
sh-Polypeptide-62 is a synthetic recombinant peptide, an analog of human Hepatocyte Growth Factor (HGF). It stimulates keratin production, hair growth, and hair pigmentation, and accelerates wound healing and skin regeneration.
Hepatocyte Growth Factor (HGF) is a multifunctional cytokine initially identified as a mitogen (growth factor) for hepatocytes (liver cells). It is now recognized as a growth factor in several human tissues.
In skin, HGF is produced by dermal fibroblasts as a response to keratinocyte-produced cytokines after UV exposure. Then it acts as a growth factor for melanocytes and keratinocytes, enhancing melanin production and protecting the skin from UV-induced damage. In the human scalp, HGF is secreted by perifollicular dermal white adipose tissue (dWAT), particularly by differentiated adipocytes, pre-adipocytes, and pericytes.
Scientists noticed that reduced perifollicular dWAT and decreased HGF secretion are common in androgenetic alopecia and alopecia areata. Conversely, excessive HGF activity may contribute to hirsutism or hypertrichosis, as suggested by hair growth following autologous fat grafting.sh-Polypeptide-62 activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling in human hair follicles, a pathway essential for anagen maintenance and keratin gene expression. Furthermore, it acts as a promelanogenic factor, stimulating melanin production specifically within the hair follicle pigmentary unit.
In vivo studies with sh-Polypeptide-62 altered hair follicle function, revealing hair shaft elongation after 2 days. In addition, Recombinant human HGF improved keratinocyte proliferation, hair pigmentation, and differentiation of hair shaft cells.
In skin care applications, sh-Polypeptide-62 intactes that interact with c-Met receptors on melanocytes and keratinocytes accelerate wound healing and recovery, enhance barrier function, and promote tanning and repigmentation. However, products containing HGF mimetics should be used with caution, as HGF overexpression is associated with the induction or progression of melanoma.