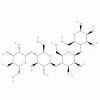
Carbohydrates
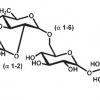
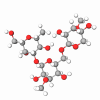
This group is composed of highly effective skincare ingredients derived from diverse natural sources, including plants, grains, fungi, and yeast. The majority of carbohydrates incorporated into beauty formulas are glucans, long chains of glucose molecules that are linked together. Being derived from plants or microorganisms, these compounds are pretty familiar to our body cells, so they don’t cause any dermal irritation or sensitization. Some of the glucans are even utilized in the food industry. They are safe in concentrations used in cosmetics.
Glucans are a total win-win for all skin types. First, these carbohydrates are exceptional moisturizers. Applied to the top layer of the epidermis, they form a delicate layer on it and, thus, hinder water evaporation from the surface of the face. On the other hand, due to their chemical structure, they can bond with water molecules and retain them within the dermal layers. The double-moisturizing effect of these molecules protects the skin from dehydration, subsequent dermal destruction, and wrinkle formation.
Next, they are potent antioxidants and anti-inflammatory agents. These carbohydrates efficiently hunt and neutralize free radicals, which are the leading cause of collagen quantity drop and wrinkling. Actively penetrating the epidermis and dermis, they also halt the harmful cascade of inflammatory processes and prevent degradation of the skin's framework.
Additionally, these compounds are involved in inhibiting melanin production. In this way, they combat hyperpigmentation, one of the most common skin aging issues. And this is not the end. Some carbs are incorporated into beauty formulations to serve as prebiotics (food for dermal microflora). Microorganisms are an essential part of our body's uppermost layer, and their bioactivity directly affects skin integrity. This is why microbiome-friendly beauty formulas are one of the trends of 2021.Taking into account all these impressive benefits of polymeric carbs, many famous beauty experts mention glucans as must-have ingredients of result–delivering skincare products.
Agar is a galactose sulfate polymer obtained from red seaweeds like Gracilaria and Gelidium and forms heat-stable, strong gels at concentrations less than 0.5%. The gel forms at 90°F and melts at 190°F, showing a high hysteresis lag.
Anhydroxylitol is a synthetic cyclic sugar derived from xylitol by dehydration in an acid medium. It is a highly water-soluble and very hygroscopic substance.
Bamboo (Bambusa Arundinacea) Powder is an all-natural mechanical exfoliator for facial and body scrubs, the finely milled bamboo powder is rich in essential minerals and silica.
Biosaccharide Gum-1 is an anionic biotechnological polysaccharide obtained by a bacterial fermentation process and is accepted for organic cosmetics. It is a moisturizing, soothing, anti-aging, and hair-sheathing cosmetic active ingredient providing a soft touch to formulations.
Our organism is controlled by a communication network that maintains physiological balance. This communication is a dynamic relationship maintained between a transmitter and a receiver through messages carried from a specific channel.
Brestine is a polymer of galactose, mannose, glucose, galacturonic acid, and glucuronic acid. It is produced by marine plankton collected from the Mer d’Iroise of Brest in Bretagne. Once isolated, the micro-organism is cultivated in a bioreactor to produce large amounts of Brestine.
Carrageenans are anhydrogalactose sulfate polymers (both gelling and non-gelling types) obtained from red seaweeds, including Eucheuma and Chondrus species.
Carrageenan is a protein-reactive gum that stabilizes protein-containing cosmetic formulations.
Ceratonia Siliqua (Locust Bean) Gum is a highly purified fraction of branched galactomannan saccharide polymers with a mannose-to-galactose ratio of 4:1. It is derived from the seeds of the legume tree Ceratonia siliqua.
Cyclodextrin is a general term for cyclic oligosaccharides (glucopyranoses) biotechnologically derived from starch by enzymatic degradation with a CGT (Cyclodextrin Glucose Transferase enzyme).
Dehydroxanthan Gum is a dehydrated xanthan gum, an anionic polymer, supplied as an off-white powder. In personal care applications, it is used as a fixative, thickener, gelling agent, and for styling aid.
Dextran is a polysaccharide (polyglucan) from glucose units composed of α-C1-C6 linked chains of different lengths. Dextrans polymer chain length varies from very short (water-soluble) to very long (insoluble).
Dextrin is a degraded starch polysaccharide in which the amylose and amylopectin present in the original starch have been partially hydrolyzed at the 1,4a D and 1,6a D linkages.
Dihydroxyacetone (1,3-Dihydroxy-2-Propanone) is a simple saccharide used in self-tanning preparations. It is a white powder with a characteristic odor, readily soluble in water and mixtures of water and ethanol.
Erythrulose is a unique four-carbon ketone sugar (ketotetrose) produced via biotechnology. Its aqueous solution is a clear, yellow, highly viscous liquid.
Glycogen is a highly branched polysaccharide consisting of glucose units found in animal tissues and plants. Its molecular weight is 106 to 107, and it is used as an animal energy source or a depo.
Guar gum is a plant polysaccharide obtained from the shrub's seeds, Cyamopsis Tetragonoloba, which, like the soybean, belongs to the Family Leguminoseae. It is a non-ionic, salt-tolerant galactomannan with excellent thickening properties.