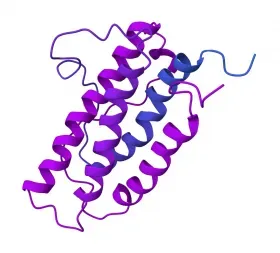
Oligopeptide-177 is a 33-amino-acid-length synthetic peptide whose sequences repeat a fragment of the erythropoietin (EPO) glycoprotein. It is a non-erythropoietic erythropoietin-derived peptide.
EPO's primary function is to stimulate the production of red blood cells (erythrocytes). Still, it also has other functions, including promoting tissue regeneration and cell protection (preventing apoptosis, or cell self-destruction).
Scientific studies have shown that the topical application of a preparation containing human recombinant erythropoietin accelerates wound healing and skin regeneration. It supports new microvessel formation, enhancing the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to regenerating tissues, while also boosting growth factor generation, resulting in skin recovery without the formation of scar tissue.
According to the manufacturer's claim, due to its specific structure (sequence), Oligopeptide-177 does not affect hematopoietic (blood cell production) processes, but maintains other beneficial functions in demand in modern skincare applications. After topical application, it can bind to the specific receptor CD90 on skin keratinocytes and fibroblasts, promoting skin regeneration, renewal, and wound healing.In manufacturer's clinical trials, Oligopeptide-177 demonstrated significant benefits for signs of skin aging, acne, and UV-induced irritation. It is one of the active ingredients in the patented complex TFC8® (Trigger Factor Complex) by Augustinus Bader, where it plays a significant role.