Today older people are still active and comfortable with their life experiences. But one sign of aging is still undesirable: pale skin. Manufacturers of body care products offer numerous anti-aging products that are specially tailored to the needs of mature skin.
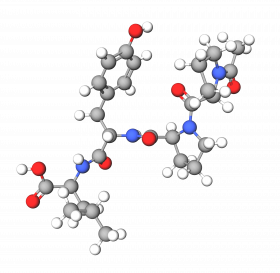
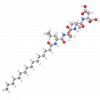
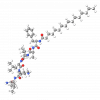
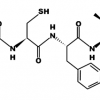
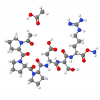
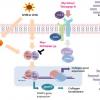
Laboratoires Sérobiologiques, the division of Cognis Care Chemicals specializing in cosmetic active ingredients, has therefore developed Acetyl Tetrapeptide-11, an active peptide with the sequence Ac-Pro-Pro-Tyr-Leu, that inhibits the effects of skin aging. It specifically targets the epidermis, which thins with age, becomes more fragile, and loses its radiance. Acetyl Tetrapeptide-11 acts on the two components of the epidermis that are mainly responsible for its cohesion, strengthening the skin's structure and giving it a smooth, youthful appearance.
The skin aging process is determined by two molecules:
- Syndecan-1 is a small proteoglycan whose production decreases with age, thereby impairing epidermal cohesion.
- Collagen XVII is a protein found in hemidesmosomes - microscopic, punctiform adhesive complexes that influence adhesion between the epidermis and the dermo-epidermal junction.
Efficacy was demonstrated in a panel of retirees aged 65 or older. Their skin now reflects their inner strength; it expresses their joy in life and their pride: aging, yes, but with beauty and grace. Acetyl Tetrapeptide-11 is suitable for use in anti-aging face creams and care products for mature skin.