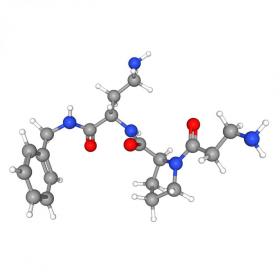
Syn-Ake (Dipeptide Diaminobutyroyl Benzylamide Diacetate) is a cutting-edge wrinkle treatment, thanks to a remodeled synthetic tripeptide, derived initially from snake (Temple Viper) venom, Waglerin-1. Mimicking the effect of Waglerin-1, this peptide relaxes muscle movement by temporarily immobilizing facial contractions that cause facial lines and wrinkles.
It reduces muscle contractions by up to 80% (in vitro results) due to the disabling of the muscular nACh receptors. Moreover, due to the reduction in micro-contractions, a significant smoothing effect can already be noticed after 28 days, accompanied by a considerable decrease in skin wrinkles, all without altering the natural radiance of the face in the process.
A recent study demonstrated that Dipeptide Diaminobutyroyl Benzylamide Diacetate exhibits noticeable antioxidant activity in a dose-dependent manner, as confirmed by DPPH free radical tests.
Syn-Ake works to relax fine lines and wrinkles, quickly and dramatically lifting sagging skin. In addition, the enhanced tri-peptide helps diminish the appearance of expression lines, firming the skin around the eyes, forehead, and mouth for a more youthful appearance. It is recommended for use in skincare, including facial moisturizers, cleansers, anti-aging serums, and creams.F.A.Q.
Is SYN®-AKE a competitive alternative to Botox® injections?
Invasive treatments, such as Botox injections and collagen fillers, are used to reverse the aging appearance temporarily. However, these treatments are expensive, unpleasant, and anyone who has ever flipped through a woman's glossy magazine can attest that some results are far from ideal.
SYN®-AKE is an innovative, non-invasive (needle-free) wrinkle treatment with a Botox-like effect that can help your complexion return to a younger, more natural, and relaxed state.