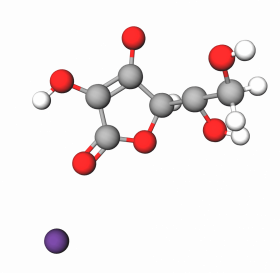
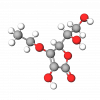
Sodium Ascorbate is a sodium salt of L-Ascorbic acid or Vitamin C, a member of a group of food additives called mineral ascorbates. Although it is primarily used in the food processing industry as an antioxidant, preservative, acidity regulator, and vitamin C supplement (E301), Sodium Ascorbate is also a valuable ingredient in personal care applications.
It has been clinically tested for treating various skin conditions and even diseases like melanoma, and has proven effective for its vitamin C-like action and for killing cancer cells. But unfortunately, Sodium ascorbate inherited the weak point of L-Ascorbic acid: instability. In formulations, it should be protected from air and light, which can break down this powerful ingredient. Thus, liposome or another type of encapsulation is crucial for the effectiveness and shelf-life of this ingredient.
Compared with pure L-Ascorbic acid, Sodium Ascorbate has better bioavailability thanks to the presence of Na+ cation. Special proteins, Sodium-dependent Vitamin C Transporters, are responsible for transferring ascorbate anion (vitamin C) into the cell. A higher sodium gradient provides a higher penetration rate.
Like vitamin C, Sodium Ascorbate is a potent antioxidant. In addition, it works well in synergy with other free-radical-scavenging molecules, such as tocopherols (vitamin E), thereby protecting cell membranes, DNA, and other structures from oxidative stress and UV-induced damage. It is an effective treatment for burn-affected skin and striae distensae (parallel striae lying perpendicular to the skin's tension lines).In addition, sodium Ascorbate exhibits all the beneficial effects of L-Ascorbic acid on the skin, including boosting collagen and elastin production, suppressing melanin synthesis, and enhancing cell metabolism and skin recovery. It is a safe anti-aging ingredient with many benefits for the skin's healthy, smooth, and bright appearance.